Focused, One-on-One Physical Therapy Treatment
Soft Tissue Mobilization
Reduce Inflammation. Increase Your Range of Motion.
Muscle strains can be painful and cause swelling, loss of range of motion, and more. The deep pressure of soft tissue mobilization can release muscle tension and move the fluids trapped in the tissue. The practice of soft tissue mobilization can be used for those with medical conditions affecting their muscle tissue, or for everyday people who have tense muscles that need stretching.

What Is Soft Tissue Mobilization?
Soft tissue mobilization is a manual physical therapy practice that uses stretching techniques to release muscle strain inflammation. It works by massaging the fascia and ligaments to move the fluids trapped in the muscle tissue.
What Are the Benefits of Soft Tissue Mobilization?
For people with injuries, one major benefit of soft tissue mobilization is that it can restore normal muscle functionality. This functionality improves as the tendons and muscles are lengthened in the stretching process and the adhesions are broken down. Other benefits of soft tissue mobilization are decreased pain, less swelling, a better range of muscle motion, and the stimulation of new connective tissue formation.
What Conditions Does Soft Tissue Mobilization Treat?
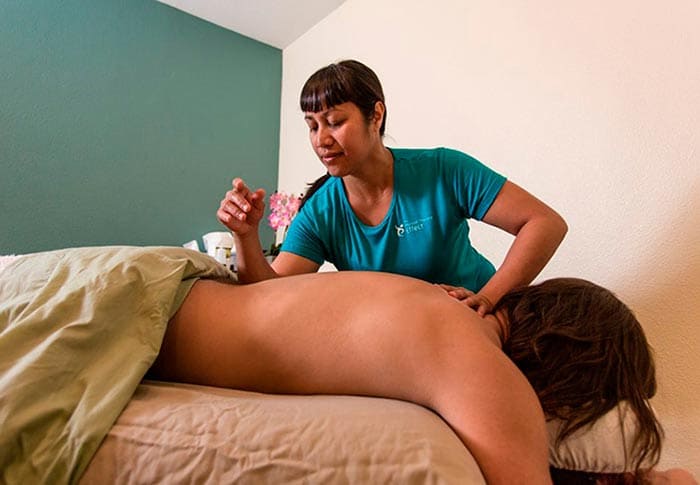

Soft tissue mobilization can treat a variety of conditions. Most commonly, it is used to treat problems in the upper or lower extremities of the body such as:
What Are Some Examples of Soft Tissue Mobilization Techniques?
Depending on where you have a muscle strain or tension, there are different types of soft tissue mobilization that a physical therapist may consider for your case.
Myofascial Release
Also known as a form of deep tissue work, myofascial release reduces tightness in focused areas of the body. It is usually used in cases of immobility or chronic muscle pain to ease muscle strain with gentle pressure application on specific trigger points.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual lymphatic drainage, or MLD, improves circulation by using firm hand movements along the lymph pathways in the body. This kind of soft tissue mobilization improves circulation in swollen legs and muscles or migraines.
Strain-Counterstrain
This type of soft tissue mobilization uses a passive position that holds pain points for up the three minutes. A physical therapist can help soften the tissue and reduce any nagging stiffness in the body after holding the position.
Parallel Mobilization
Parallel mobilization is a technique that pushes along the seams of the muscles. By pushing along the seams, the therapist can manipulate the physical function of the tissues and reduce pain.
Friction Massage
Pushing along the ligaments or tendons is called a friction massage. This involves going across the muscle grain and pushing firmly into pressure points. In areas that are especially tight, a friction massage can increase circulation. In a friction massage, a therapist will apply pressure with their fingertips on the sore muscles or tendons.
Unlocking Spiral
By alternating between clockwise or counterclockwise motions, this technique pushes on the tense tissue continuously through the circular motion to move the fluid that is trapped. This is usually a rhythmic pushing that is done repeatedly until there is inflammation relief.
What Are the Risks of Soft Tissue Mobilization?

Every physical therapy practice involves an assessment of risk versus reward. For some individuals with pre-existing health conditions, the risk of soft tissue mobilization may outweigh the benefits. If you have any of the below conditions, always consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing any new treatment.